library(lares)
library(tidyverse)
library(tidymodels)
library(themis)
library(tidyposterior)
library(SmartEDA)
library(DataExplorer)
library(skimr)
library(ggpubr)
library(workflowsets)Penanganan Class Imbalanced pada KNN dengan tidymodels
Package
Deskripsi singkat data
Tutorial kali ini akan menggunakan data yaitu German df. Berikut adalah informasi singkat mengenai data
This dataset classifies people described by a set of attributes as good or bad df risks.
Author: Dr. Hans Hofmann Source: UCI - 1994 Please cite: Dua, D. and Graff, C. (2019). UCI Machine Learning Repository [http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml]. Irvine, CA: University of California, School of Information and Computer Science.
Attribute description
- Status of existing checking account, in Deutsche Mark.
- df history (dfs taken, paid back duly, delays, critical accounts)
- Purpose of the df (car, television,…)
- df amount
- Status of savings account/bonds, in Deutsche Mark.
- Present employment, in number of years.
- Installment rate in percentage of disposable income
- Personal status (married, single,…) and sex
- Other debtors / guarantors
- Present residence since X years
- Property (e.g. real estate)
- Age in years
- Other installment plans (banks, stores)
- Housing (rent, own,…)
- Number of existing dfs at this bank
- Job
- Number of people being liable to provide maintenance for
- Telephone (yes,no)
- Foreign worker (yes,no)
- Duration in months
data ini bisa diperoleh di link berikut ini
Import data di R
df <- read_csv("german_credit.csv") %>%
# convert all character column to factor
mutate(across(where(is.character),as.factor))Rows: 1000 Columns: 21
── Column specification ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
Delimiter: ","
chr (14): checking_status, credit_history, purpose, savings_status, employme...
dbl (7): duration, credit_amount, installment_commitment, residence_since, ...
ℹ Use `spec()` to retrieve the full column specification for this data.
ℹ Specify the column types or set `show_col_types = FALSE` to quiet this message.glimpse(df)Rows: 1,000
Columns: 21
$ checking_status <fct> '<0', '0<=X<200', 'no checking', '<0', '<0', 'n…
$ duration <dbl> 6, 48, 12, 42, 24, 36, 24, 36, 12, 30, 12, 48, …
$ credit_history <fct> 'critical/other existing credit', 'existing pai…
$ purpose <fct> radio/tv, radio/tv, education, furniture/equipm…
$ credit_amount <dbl> 1169, 5951, 2096, 7882, 4870, 9055, 2835, 6948,…
$ savings_status <fct> 'no known savings', '<100', '<100', '<100', '<1…
$ employment <fct> '>=7', '1<=X<4', '4<=X<7', '4<=X<7', '1<=X<4', …
$ installment_commitment <dbl> 4, 2, 2, 2, 3, 2, 3, 2, 2, 4, 3, 3, 1, 4, 2, 4,…
$ personal_status <fct> 'male single', 'female div/dep/mar', 'male sing…
$ other_parties <fct> none, none, none, guarantor, none, none, none, …
$ residence_since <dbl> 4, 2, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4, 2, 4, 2, 1, 4, 1, 4, 4, 2,…
$ property_magnitude <fct> 'real estate', 'real estate', 'real estate', 'l…
$ age <dbl> 67, 22, 49, 45, 53, 35, 53, 35, 61, 28, 25, 24,…
$ other_payment_plans <fct> none, none, none, none, none, none, none, none,…
$ housing <fct> own, own, own, 'for free', 'for free', 'for fre…
$ existing_credits <dbl> 2, 1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 1,…
$ job <fct> skilled, skilled, 'unskilled resident', skilled…
$ num_dependents <dbl> 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,…
$ own_telephone <fct> yes, none, none, none, none, yes, none, yes, no…
$ foreign_worker <fct> yes, yes, yes, yes, yes, yes, yes, yes, yes, ye…
$ class <fct> good, bad, good, good, bad, good, good, good, g…Penanganan Imbalanced Data
df %>%
count(class) %>%
rename(cat=class) %>%
mutate(label=str_c(cat,"(",n,"/",
round(n*100/sum(n),2),"%)")
) %>%
ggdonutchart(x="n",label = "label",
fill = c("#962E10","#107896"),
lab.pos = "out",
lab.font = c(5,"bold","black")
)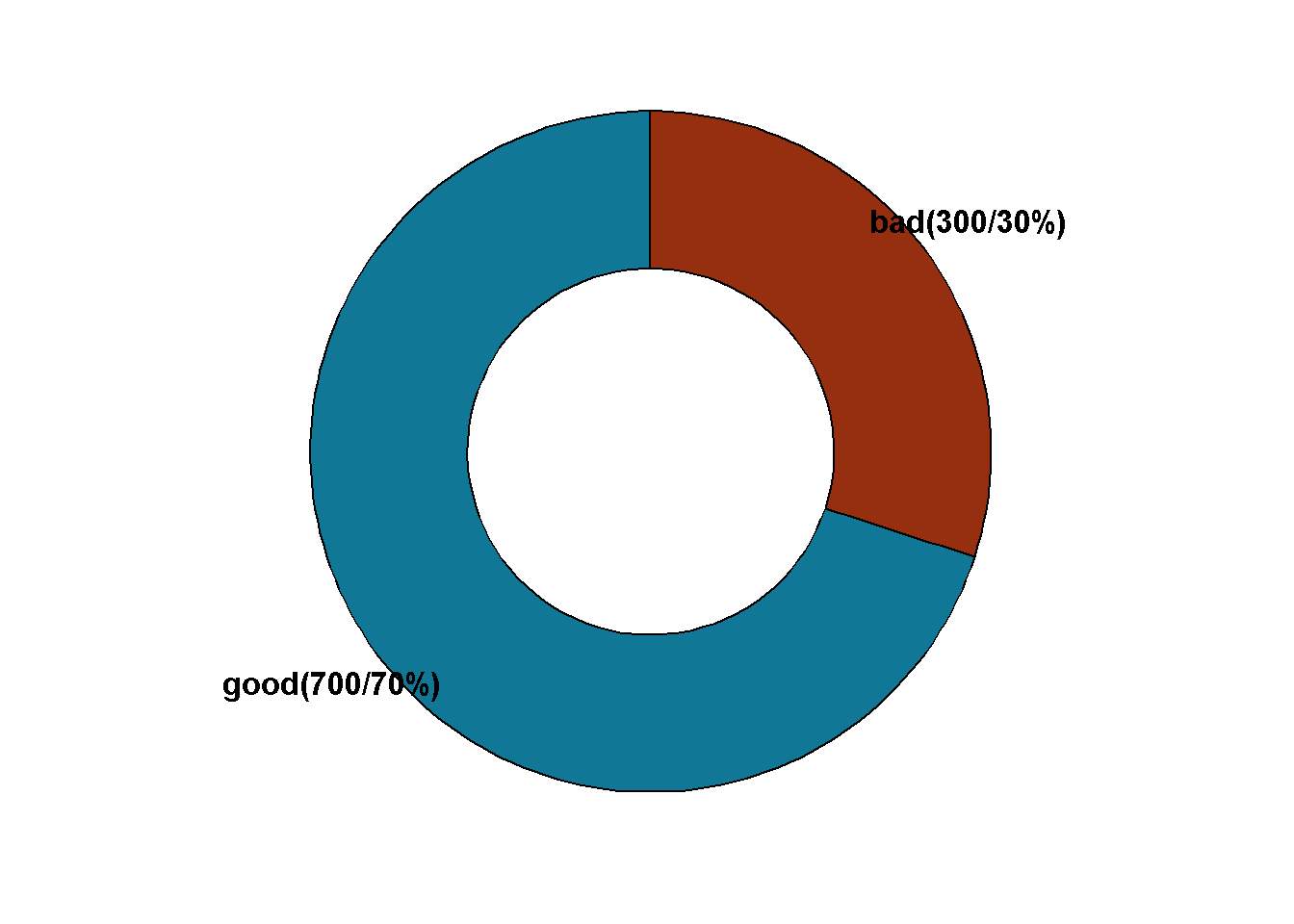
Random Over sampling (ROS)
upsm_try <- map(seq(0.5,1.25,0.25),function(x) {
recipe(class~.,data = df) %>%
step_upsample(class,over_ratio = x,skip = FALSE) %>%
prep() %>%
bake(new_data = df) %>%
count(class,name = str_c("Oversampling ",x))
})
upsm_try[[1]]
# A tibble: 2 × 2
class `Oversampling 0.5`
<fct> <int>
1 bad 350
2 good 700
[[2]]
# A tibble: 2 × 2
class `Oversampling 0.75`
<fct> <int>
1 bad 525
2 good 700
[[3]]
# A tibble: 2 × 2
class `Oversampling 1`
<fct> <int>
1 bad 700
2 good 700
[[4]]
# A tibble: 2 × 2
class `Oversampling 1.25`
<fct> <int>
1 bad 875
2 good 875Output diatas adalah efek pemilihan over_ratio terhadap pertambahan class minority bad. Selanjutnya kita pilih over_ratio=1
upsm <- recipe(class~.,data = df) %>%
step_upsample(class,over_ratio = 1) Random Under sampling (RUS)
undersm_try <- map(seq(0.5,1.25,0.25),function(x) {
recipe(class~.,data = df) %>%
step_downsample(class,under_ratio = x,skip = FALSE) %>%
prep() %>%
bake(new_data = df) %>%
count(class,name = str_c("Undersampling ",x))
})
undersm_try[[1]]
# A tibble: 2 × 2
class `Undersampling 0.5`
<fct> <int>
1 bad 150
2 good 150
[[2]]
# A tibble: 2 × 2
class `Undersampling 0.75`
<fct> <int>
1 bad 225
2 good 225
[[3]]
# A tibble: 2 × 2
class `Undersampling 1`
<fct> <int>
1 bad 300
2 good 300
[[4]]
# A tibble: 2 × 2
class `Undersampling 1.25`
<fct> <int>
1 bad 300
2 good 375Output diatas adalah efek pemilihan under_ratio terhadap pengurangan class majority good. Selanjutnya kita pilih under_ratio=1
undersm <- recipe(class~.,data = df) %>%
step_downsample(class,under_ratio = 1)Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique (SMOTE)
Penerapan metode SMOTE hanya bisa dilakukan untuk peubah prediktor numerik. Jika terdapat peubah prediktor kategorik seperti pada data ini, maka terdapat dua solusi yang mungkin yaitu:
- Menggunakan metode SMOTE-NC (baca jurnal di link berikut) yang bisa diterapkan di peubah prediktor kategorik maupun peubah prediktor numerik. Namun, SMOTE-NC belum tersedia di ekosistem
mlr3(November 2021). - Melakukan Categorical Variable Encoding, yaitu transformasi peubah prediktor kategorik ke peubah prediktor numerik. Metode-metode apa saja yang termasuk Categorical Variable Encoding bisa dilihat pada link berikut ini
Fungsi step_smote dari package themis menggunakan metode SMOTE yang hanya bisa diterapkan pada prediktor numerik saja
smote_try <- try(map(seq(0.5,1.25,0.25),function(x) {
recipe(class~.,data = df) %>%
step_smote(class,over_ratio = x,skip = FALSE) %>%
prep() %>%
bake(new_data = df) %>%
count(class,name = str_c("Undersampling ",x))
}))Error in map(seq(0.5, 1.25, 0.25), function(x) { : ℹ In index: 1.
Caused by error in `step_smote()`:
Caused by error in `prep()`:
✖ All columns selected for the step should be double or integer.
• 13 factor variables found: `checking_status`, `credit_history`, …Sementara itu jika prediktor yang dimiliki terdapat prediktor numerik dan prediktor kategorik bisa menggunakan fungsi step_smotenc dari package themis
smote_try <- map(seq(0.5,1.25,0.25),function(x) {
recipe(class~.,data = df) %>%
step_smotenc(class,over_ratio = x,skip = FALSE) %>%
prep() %>%
bake(new_data = df) %>%
count(class,name = str_c("Undersampling ",x))
})
smote_try[[1]]
# A tibble: 2 × 2
class `Undersampling 0.5`
<fct> <int>
1 bad 350
2 good 700
[[2]]
# A tibble: 2 × 2
class `Undersampling 0.75`
<fct> <int>
1 bad 525
2 good 700
[[3]]
# A tibble: 2 × 2
class `Undersampling 1`
<fct> <int>
1 bad 700
2 good 700
[[4]]
# A tibble: 2 × 2
class `Undersampling 1.25`
<fct> <int>
1 bad 875
2 good 875Output diatas adalah efek pemilihan over_ratio terhadap pertambahan class minority bad. Selanjutnya kita pilih over_ratio=1
smote_fin <- recipe(class~.,data = df) %>%
step_smotenc(class,over_ratio = 1) Pemodelan KNN
Menyiapkan Pembagian Data
K-fold Cross Validation
set.seed(345)
folds <- vfold_cv(df, v = 10,strata = "class")Contoh visualisasi 100 amatan pertama di setiap folds
tidy(folds) %>%
filter(Row<101) %>%
ggplot(aes(x = Fold, y = Row,fill = Data)) +
geom_tile()+
theme_lares()Warning in .font_global(font, quiet = FALSE, ...): Font(s) "Arial Narrow" not
installed, with other name, or can't be found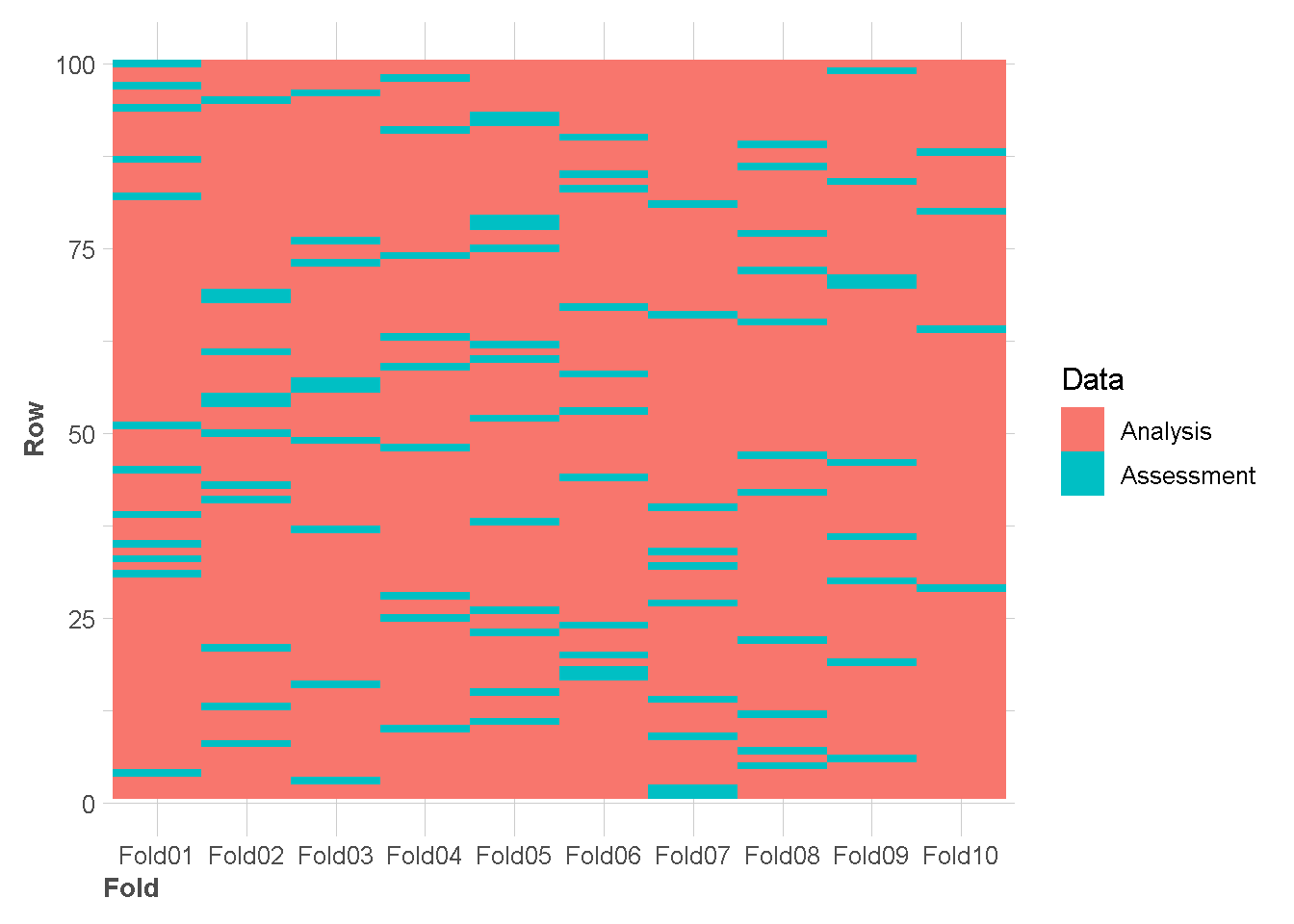
Mendefinisikan Model KNN
knn_tune <- nearest_neighbor(neighbors=tune(),
weight_func="rectangular") %>%
set_engine("kknn") %>%
set_mode("classification")knn_grid <- grid_regular(neighbors(range = c(2,50)),
levels= 50)
knn_grid Komparasi, Tuning dan Evaluasi Model
Menkombinasikan metode class imbalanced dan model
models <- list(knn=knn_tune)
preproc <- list(over_sample=upsm,
under_sample=undersm,
smote=smote_fin)
wf_set <- workflow_set(preproc = preproc,models = models)Running models
models_eval <- workflow_map(wf_set,
fn="tune_grid",
resamples = folds,
control=control_grid(save_workflow = TRUE),
metrics=metric_set(accuracy,
bal_accuracy),
grid = knn_grid,
seed = 2123)Evaluasi model
## custom function
extract_neighbor <- function(wflw_res) {
map(seq_along(wflw_res$wflow_id), function(i) {
id <- wflw_res$wflow_id[i]
res <- extract_workflow_set_result(wflw_res, id = id) %>%
collect_metrics() %>%
mutate(wflow_id = id,
.config = NULL,
.estimator = NULL) %>%
relocate(wflow_id)
return(res)
}) %>%
list_rbind()
}## custom function
plot_neighbor<- function(knn_result,metric){
knn_result %>%
filter(.metric%in%metric) %>%
mutate(wflow_id=str_remove_all(wflow_id,"_knn")) %>%
ggplot(aes(x=neighbors, y=mean,col=wflow_id)) +
geom_line()+
geom_point()+
ylab(metric) +
scale_x_continuous(n.breaks = 12)+
theme_lares()+
theme(legend.position = "top")
}## metric used information
metric_used <- models_eval %>%
collect_metrics() %>%
pull(.metric) %>%
unique()
metric_used[1] "accuracy" "bal_accuracy"neighbors_result <- extract_neighbor(models_eval)
neighbors_result %>%
plot_neighbor(metric = metric_used[1])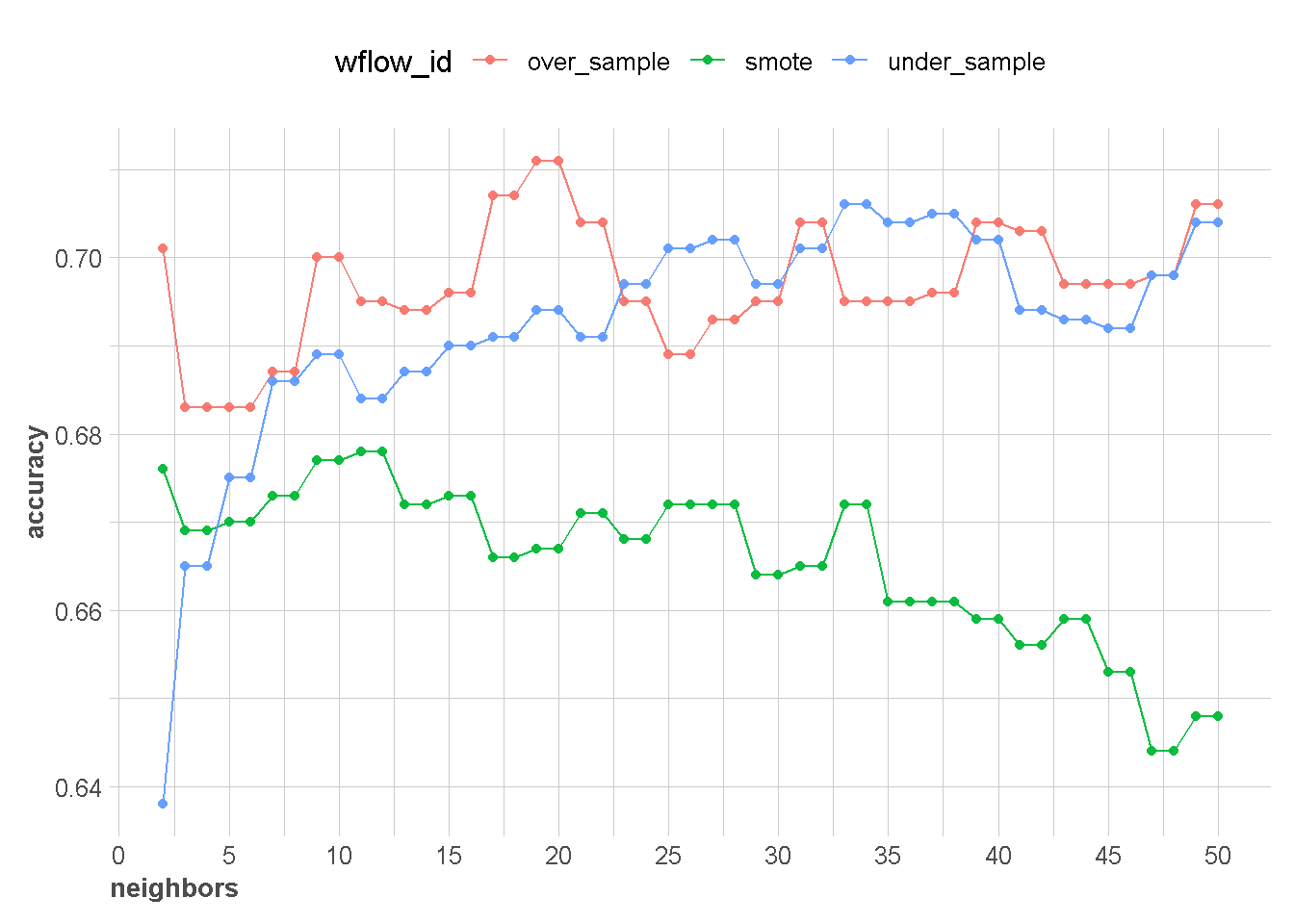
neighbors_result %>%
plot_neighbor(metric = metric_used[2])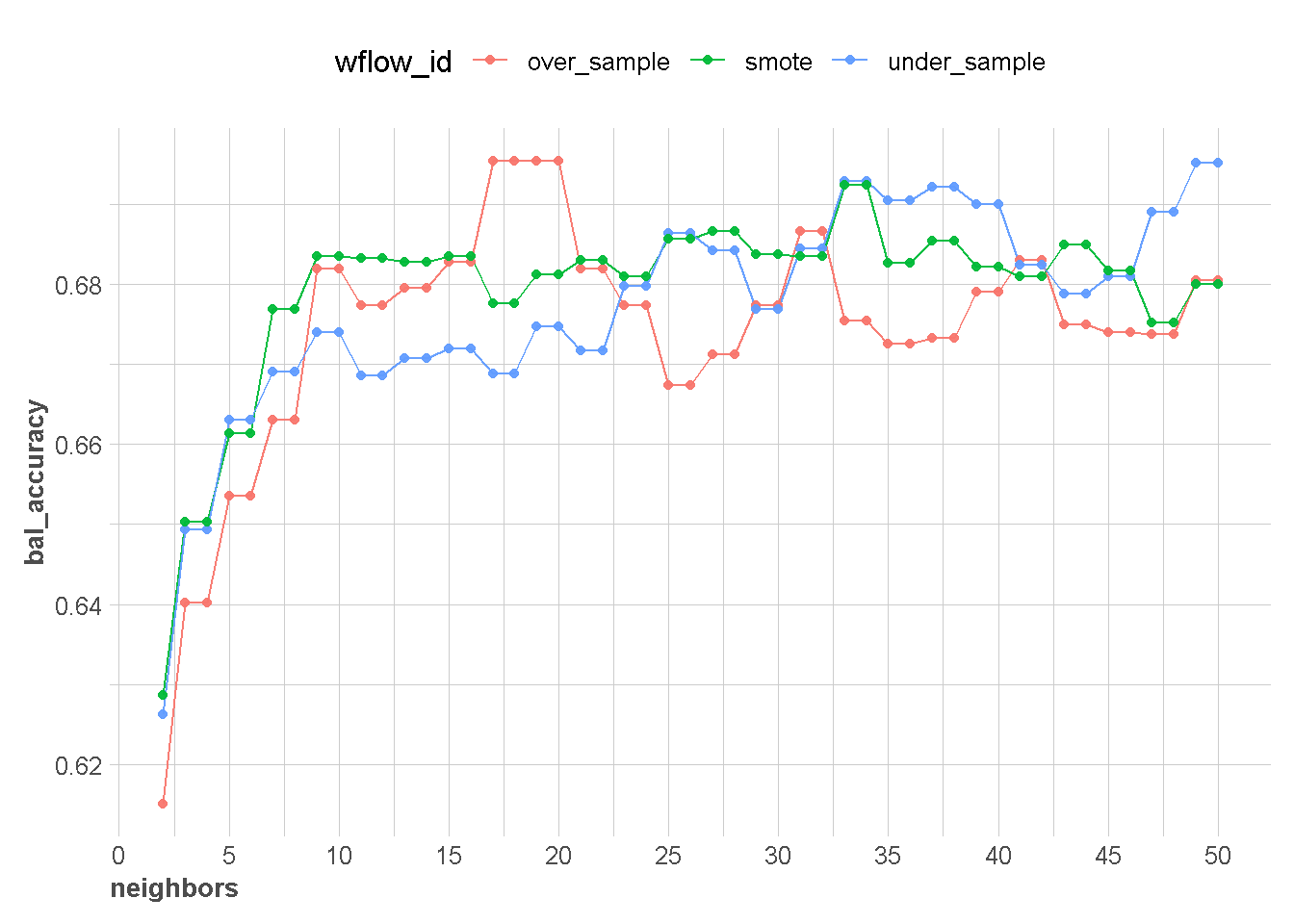
Menentukan Model terbaik dan Training
mod_best1 <- fit_best(x = models_eval,metric = "accuracy")
mod_best1══ Workflow [trained] ══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════
Preprocessor: Recipe
Model: nearest_neighbor()
── Preprocessor ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
1 Recipe Step
• step_upsample()
── Model ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
Call:
kknn::train.kknn(formula = ..y ~ ., data = data, ks = min_rows(19L, data, 5), kernel = ~"rectangular")
Type of response variable: nominal
Minimal misclassification: 0.2628571
Best kernel: rectangular
Best k: 19mod_best2 <- fit_best(x = models_eval,metric = "bal_accuracy")
mod_best2══ Workflow [trained] ══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════
Preprocessor: Recipe
Model: nearest_neighbor()
── Preprocessor ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
1 Recipe Step
• step_upsample()
── Model ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
Call:
kknn::train.kknn(formula = ..y ~ ., data = data, ks = min_rows(17L, data, 5), kernel = ~"rectangular")
Type of response variable: nominal
Minimal misclassification: 0.2578571
Best kernel: rectangular
Best k: 17Prediksi Data baru
Berikut kita generate data baru dummy
set.seed(1234)
data_baru <- df %>%
slice_sample(n = 2,by = class) %>%
select(-class)
data_barupred_data_baru2 <- mod_best1 %>%
predict(new_data = data_baru)
pred_data_baru3 <- mod_best2 %>%
predict(new_data = data_baru)pred_data_baru2pred_data_baru3